Used in large-scale ventilation systems worldwide, bi-polar ionization could be a secret weapon in the war against COVID-19
Companies are scrambling to test bi-polar ionization systems against the coronavirus. Bi-polar ionization technology releases charged atoms that attach to and deactivate harmful substances like bacteria, mold, allergens, and viruses. It first arrived in the United States in the 1970s as a tool to control pathogens in food manufacturing.
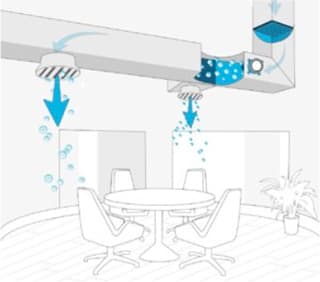
Bi-polar ionization has already proven effective against SARS, norovirus, and several influenza strains. Bi-polar ionization is experiencing a surge in popularity as the coronavirus pandemic fans are concerned about air quality. Integrated into HVAC systems, the technology utilizes specialized tubes that take oxygen molecules from the air and convert them into charged atoms that then cluster
around microparticles, surrounding and deactivating harmful substances like airborne mold, bacteria, allergens, and viruses.
They also attach to expelled breath droplets and dust particles that can transport viruses, enlarging them so they’re more easily caught in filters. It’s an active process that provides continuous disinfection.
“The ions produce a chemical reaction on the cell membrane surface that inactivates the virus,” Philip Tierno, a clinical professor of microbiology and pathology at the NYU School of Medicine, told Business Insider. “It can reduce 99.9% of microbes in a matter of minutes.”
The battle against the coronavirus could be an air fight
Concerns about airborne transmission have grown as new research indicates the novel coronavirus can remain airborne longer and spread further than previously thought. Some experts now believe that just normal breathing can spread the virus.
“The possibility of aerosolized spread of COVID-19 and the ability of particles to hang in the air for extended periods of time would make the consideration of an active air-cleaning strategy even more prudent.”
Long popular in Europe, bi-polar ionization first arrived in the United States in the 1970s as a tool to control
pathogens in food manufacturing. It was effective during the SARS outbreak of 2004, as well as more recent outbreaks of MERS and norovirus and various strains of influenza. Recent advances have made units cheaper and easier to install and companies are scrambling to test the technology against the coronavirus.
Tierno said, early results have been positive: “Because corona viruses are enveloped viruses, they are easier to kill compared to naked viruses like noroviruses.”
Many large venues already employ bi – polar ionization
Hospital Boston and the University of Maryland Medical Center, Terminals at LaGuardia, O’Hare, LAX, and San Francisco International Airport Tampa’s Amalie Arena, and the TWA Hotel at JFK Airport are adopting NBPI, as are large workplaces such as Google’s headquarters in Chicago and San Jose. In addition, ionization reduces the volume of outside air replenishment thus reducing utility costs.
Bi-polar Ionization is a TRUE weapon in the COVID-19 battle, but it also carries massive cost-savings potential.
Energy savings from bi-polar Ionization (NBPI) retrofits can vary based on size and quantity of equipment, but basically, the savings is derived from two factors:
Air recirculation and coil maintenance
The maintenance savings as a result of the device keeping the coil clean is variable depending on the cleaning schedule. The bulk of the savings comes from being able to recirculate indoor air rather than having to use energy to draw in and condition outdoor air.
According to ASHRAE 62 Indoor Air Quality Procedure (IAQP), combined with NPBI technology, outside air intake may be reduced by up to 75% in non-healthcare applications, subject to building pressure. The IAQP allows air purification to be applied to clean the air within the building and remove the contaminants of concern, thus reducing the outside air intake needed for dilution.

NPBI technology controls and/or destroys the contaminants of concern; therefore, less outdoor air requires conditioning, resulting in significant energy savings. NPBI has been installed in over 1,000 projects with the ventilation rates reduced to 5 CFM per person or less. For example, in a K-12 application in the southeast United States, on a 100,000 square feet school, the typical first
cost savings are $500,000, and the annual energy savings are generally $0.25 to $0.40 per square foot.
It is always best to create a custom proposal for each client in an attempt to be as accurate as possible, but in theory, based on an annual use of 1,800 hours, you can assume $8-10K savings for a 25-ton AHU or $5-6K savings for a 15-ton AHU. Our analysis/consultation is always free. All we need is a copy of the mechanical drawings, a copy of your maintenance. Logs, three recent utility bills (all pages) and authorization to let us view your electricity usage history from the provider. The added value is that this technology is proven to strip 90% of corona viruses from the air.
We offer a no-money down plan, and the cost is lessened by energy savings.
Discover Independence Through Using The Power Of Solar Panels!
We offer products, solutions, and services across the entire energy value chain. We support our customers on their way to a more sustainable future – no matter where you are in your search for sustainable energy independence.
